Wprowadzenie do wzorców w C #
Wzory są powtarzalnym wzorem dekoracyjnym. Istnieje prosty kod do pisania wzorców w języku C #. Możemy napisać kod, aby wydrukować różne rodzaje wzorów, takie jak wzór gwiazdy, wzór znaku i wzór liczbowy. Poniżej znajdują się różne przykłady drukowania wzorów gwiazd, znaków i wartości liczbowych. Te przykłady składają się z pętli lub zagnieżdżonych pętli, które są pętlą wewnątrz pętli. Wzory są sposobem projektowania sekwencyjnego lub logicznego. Możemy drukować trójkąty, piramidy, diamenty i inne symetrie.
Top 3 rodzaje wzorów w C #
Top 3 typy wzorów w c # są wymienione poniżej.
1. Wzór gwiazdy
Poniżej podano przykłady drukowania wzorów gwiazd.
Przykład 1
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace StarPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y, z;
for (x =6; x >= 1; x--)
(
for (y = 1; y < x; y++)
(
Console.Write(" ");
)
for (z = 6; z >= x; z--)
(
Console.Write("*");
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Wynik:

Przykład nr 2
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace StarPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
for (x = 1; x <= 6; x++)
(
for (y = 1; y <= x; y++)
(
Console.Write("*");
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Wynik:

Przykład nr 3
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace StarPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
for (x = 5; x >= 1; x--)
(
for (y = 1; y <= x; y++)
(
Console.Write("*");
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Wynik:

Przykład 4
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace StarPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y, z;
for (x = 5; x >= 1; x--)
(
for (y = 5; y > x; y--)
(
Console.Write(" ");
)
for (z = 1; z <=x; z++)
(
Console.Write("*");
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Wynik:

Przykład 5
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace StarPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y, z;
for (x= 1; x <= 5; x++)
(
for (y = x; y < 5; y++)
(
Console.Write(" ");
)
for (z = 1; z < (x * 2); z++)
(
Console.Write("*");
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Wynik:

Przykład nr 6
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace StarPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y, z;
for (x = 5; x >= 1; x--)
(
for (y = 5; y > x; y--)
(
Console.Write(" ");
)
for (z = 1; z < (x * 2); z++)
(
Console.Write("*");
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Wynik:

Przykład nr 7
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace StarPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
for (x = 1; x <= 5; x++)
(
for (y = x; y < 5; y++)
(
Console.Write(" ");
)
for (y = 1; y <= (2 * x - 1); y++)
(
if (x == 5 || y == 1 || y == (2 * x - 1))
(
Console.Write("*");
)
else
(
Console.Write(" ");
)
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Wynik:

Przykład nr 8
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace CharacterPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
for (x = 1; x <= 5; x++)
(
for (y = 1; y <= 5; y++)
(
Console.Write("*");
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Wynik:

Przykład nr 9
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace CharacterPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
for (x = 1; x <= 5; x++)
(
for (y = 1; y <= x; y++)
(
if (y == 1 || y== x || x == 5)
(
Console.Write("*");
)
else
(
Console.Write(" ");
)
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Wynik:

2. Wzory liczbowe
Poniżej podano przykłady drukowania wzorów numerycznych.
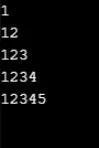
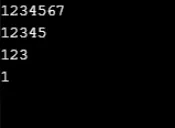
Przykład 1
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace NumberPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
for (x = 1; x <= 5; x++)
(
for (y = 1; y <= x; y++)
(
Console.Write(y);
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Wynik:
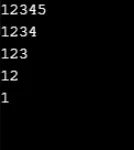
Przykład nr 2
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace NumberPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
for (x = 5; x >= 1; x--)
(
for (y = 1; y <= x; y++)
(
Console.Write(y);
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Wynik:
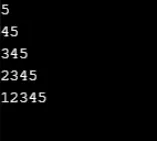
Przykład nr 3
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace NumberPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
for (x = 5; x >= 1; x--)
(
for (y = x; y <= 5; y++)
(
Console.Write(y);
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Wynik:
Przykład 4
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace NumberPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
for (x = 1; x <= 5; x++)
(
for (y = x; y <= 5; y++)
(
Console.Write(y);
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Wynik:
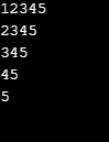
Przykład 5
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace NumberPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
for (x = 1; x <= 5; x++)
(
for (y = 1; y <= x; y++)
(
Console.Write(x);
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Wynik:
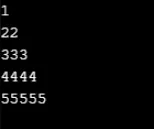
Przykład nr 6
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace NumberPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
for (x = 5; x >= 1; x--)
(
for (y = 5; y >= x; y--)
(
Console.Write(x);
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Wynik:
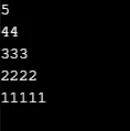
Przykład nr 7
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace NumberPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
for (x = 5; x >= 1; x--)
(
for (y = 1; y <= x; y++)
(
Console.Write(x);
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Wynik:
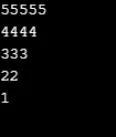
Przykład nr 8
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace NumberPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
for (x = 1; x <= 5; x++)
(
for (y = 5; y >= x; y--)
(
Console.Write(x);
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Wynik:
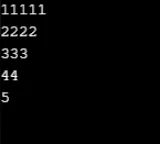
Przykład nr 9
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace NumberPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
for (x = 6; x >= 1; x--)
(
for (y = x; y >= 1; y--)
(
Console.Write(y);
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Wynik:
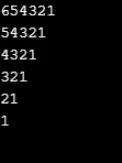
Przykład nr 10
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace NumberPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
for (x = 1; x <= 5; x++)
(
for (y = 6; y >= x; y--)
(
Console.Write(y);
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Wynik:
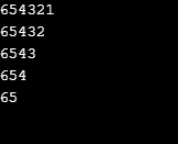
Przykład nr 11
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace NumberPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
for (x = 7; x >= 1; x -= 2)
(
for (y = 1; y <= x; y++)
(
Console.Write(y);
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Wynik:
3. Wzór postaci
The Poniżej podano przykłady drukowania wzorów znaków.
Przykład 1
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace CharacterPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
int z = 5;
for (x = 1; x <= z; x++)
(
for (y = 1; y <= x; y++)
(
Console.Write((char)(x + 64));
)
Console.WriteLine("");
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Wynik:
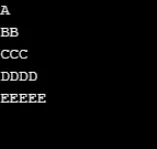
Przykład nr 2
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace CharacterPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
int z = 5;
for (x = 1; x <= z; x++)
(
for (y = x; y <= z; y++)
(
Console.Write((char)(x + 64));
)
Console.WriteLine("");
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Wynik:
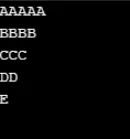
Przykład nr 3
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace CharacterPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
int z = 5;
for (x = 1; x <= z; x++)
(
for (y = 1; y <= x; y++)
(
Console.Write((char)(z - x + 1 + 64));
)
Console.WriteLine("");
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Wynik:
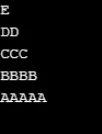
Przykład 4
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace CharacterPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
int z = 5;
for (x = 1; x <= z; x++)
(
for (y = x; y<= z; y++)
(
Console.Write((char)(y + 64));
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Wynik:
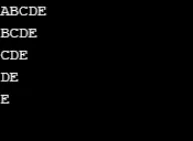
Przykład 5
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace CharacterPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y, z;
int k = 5;
for (x = 1; x <= k; x++)
(
for (y = 1; y <= k - x; y++)
(
Console.Write(" ");
)
for (z = 1; z <= x; z++)
(
Console.Write((char)(x + 64));
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Wynik:

Przykład nr 6
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace CharacterPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
int a = 5;
for (x = 1; x <= a; x++)
(
for (y = x; y >= 1; y--)
(
Console.Write((char)(y + 64));
)
Console.WriteLine("");
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Wynik:
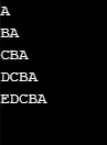
Przykład nr 7
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace CharacterPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
int a = 5;
for (x = a; x >= 1; x--)
(
for (y = a; y >= x; y--)
(
Console.Write((char)(y + 64));
)
Console.WriteLine("");
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Wynik:
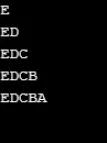
Przykład nr 8
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace CharacterPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
int a = 5;
for (x = 1; x <= a; x++)
(
for (y = a; y >= x; y--)
(
Console.Write((char)(y + 64));
)
Console.WriteLine("");
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Wynik:
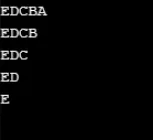
Przykład nr 9
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace CharacterPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
int z = 5;
for (x = z; x >= 1; x--)
(
for (y = x; y >= 1; y--)
(
Console.Write((char)(y + 64));
)
Console.WriteLine("");
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Wynik:
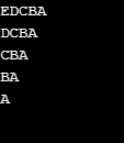
Przykład nr 10
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace CharacterPattern
(
class Program
(
static void Main(string() args)
(
int x, y;
int z = 6;
for (x = 1; x <= z; x++)
(
for (y = 1; y<= z - x; y++)
(
Console.Write(" ");
)
for (y = 1; y <= x; y++)
(
Console.Write((char)(y + 64));
)
for (y = x - 1; y >= 1; y--)
(
Console.Write((char)(y + 64));
)
Console.WriteLine();
)
Console.ReadLine();
)
)
)
Wynik:

Wniosek
Więc powyżej znajdują się przykłady różnych rodzajów wzorów. Możemy wydrukować dowolny wzór z pewnymi zmianami w pętlach.
Polecane artykuły
To jest przewodnik po Wzorach w C #. Tutaj omawiamy wprowadzenie i 3 główne typy Wzorów w C # wraz z jego przykładami i implementacją kodu. Możesz także przejrzeć następujące artykuły, aby dowiedzieć się więcej-
- Co to jest wzorzec projektowy w C #?
- Wywiad C # Design Pattern Pytania
- Tablice 2D w C #
- Przesłanianie w C #
- Przesłanianie w Javie
- 3 różne typy tablic w PHP (przykłady)
- Wzory liczbowe w Javie z przykładami